
Minimum Wage Debates: Economic Implications and Social Impact
The minimum wage debate is a longstanding and complex issue that encompasses both economic implications and social impact. Advocates argue that raising the minimum wage can improve the livelihoods of low-income workers, while critics contend that it may lead to job losses and higher inflation. This debate has gained renewed attention in recent years as discussions about income inequality and the cost of living have intensified. Examining the economic consequences and social ramifications underlines the multifaceted nature of the minimum wage debates.
Economic Implications
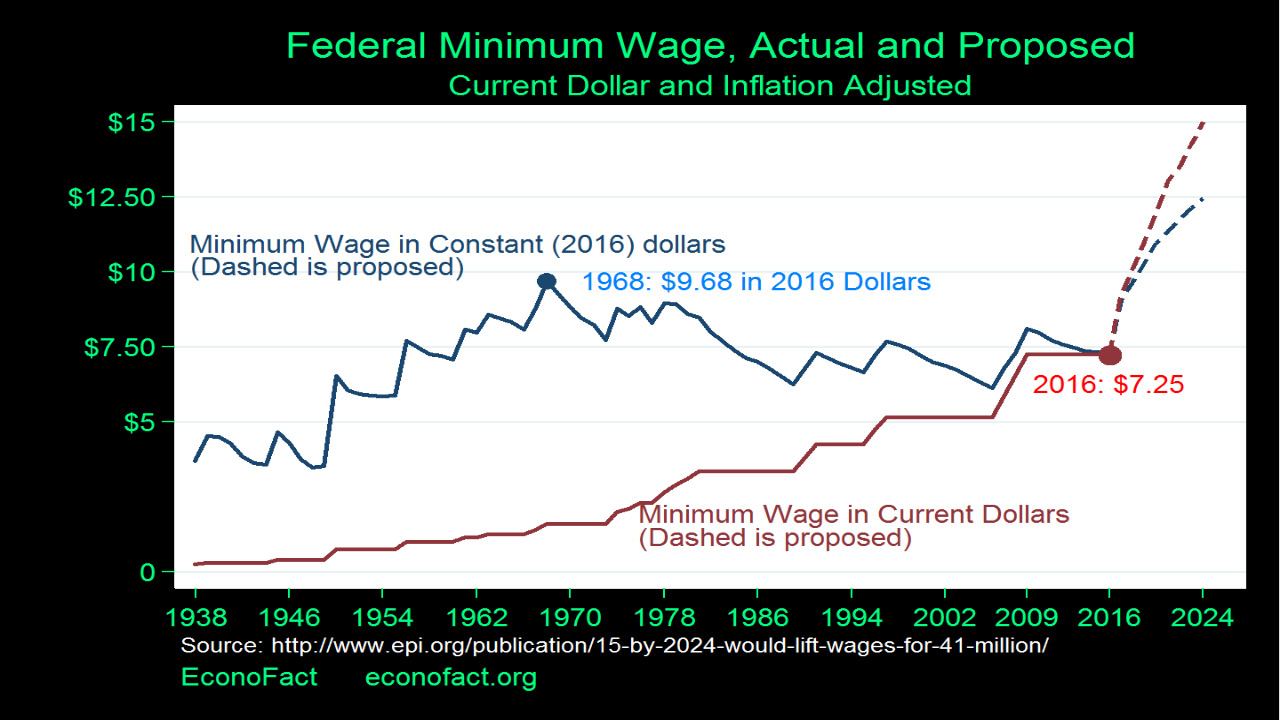
Effect on Employment: One of the central points of contention in the minimum wage debate is its potential impact on employment. Advocates of a higher minimum wage assert that increasing wages for low-income workers can stimulate consumer spending and reduce turnover, thereby enhancing productivity and economic growth. For instance, when workers have access to better wages, they might have more financial stability and be more likely to access essential services and resources. This could lead to improvements in overall well-being and job satisfaction, potentially resulting in lower turnover rates. Additionally, the availability of pay stubs online can offer employees easier access to their wage information, promoting transparency and trust between employers and workers. However, critics argue that a higher minimum wage could lead to job losses, especially among small businesses that might struggle to afford increased labor costs. Economists remain divided on this issue, with some studies suggesting a modest effect on employment and others indicating more substantial consequences.
Inflation and Pricing: Another economic implication of raising the minimum wage is its potential to trigger inflation. As businesses face higher labor costs, they may pass on these expenses to consumers in the form of higher prices for goods and services. This price increase could, in turn, erode the purchasing power of consumers, particularly those who do not experience a proportional increase in their wages. Balancing the potential benefits for workers with the risk of inflation requires careful consideration.
Social Impact

Poverty Alleviation: Proponents of raising the minimum wage often highlight its role in alleviating poverty and improving the living standards of low-income individuals and families. By providing workers with a higher baseline income, advocates argue that the minimum wage can help reduce reliance on social safety net programs and improve overall economic well-being. This perspective aligns with efforts to address income inequality and create a fairer society.
Gender and Racial Equality: The minimum wage debate also intersects with issues of gender and racial equality. Research has shown that a significant portion of minimum wage earners are women and people from marginalized communities. Advocates emphasize that raising the minimum wage can help narrow wage gaps, providing a stepping stone toward greater economic equity. However, opponents caution that the impact on certain industries, such as service and retail, may disproportionately affect women and minority workers.
Regional Disparities
Cost of Living Variations: A key factor in the minimum wage debate is the wide variation in the cost of living across different regions. While a higher minimum wage might be feasible in high-cost urban areas, it could pose challenges for businesses in regions with lower costs of living. Establishing a uniform minimum wage across the entire country might not adequately address these regional disparities and could inadvertently lead to unintended consequences.
Finding Common Ground
Navigating the minimum wage debate requires a comprehensive understanding of its economic and social implications. Policymakers must carefully weigh the potential benefits of lifting low-income workers out of poverty and promoting economic equality against the concerns surrounding job loss and inflation. A nuanced approach could involve considering different wage levels for varying regional economies and industries. Furthermore, focusing on complementary policies, such as expanding access to education and job training, could help mitigate the potential negative effects of a higher minimum wage.
In conclusion, the minimum wage debate remains a multifaceted issue with far-reaching implications. It involves a delicate balance between addressing income inequality and the potential for economic disruptions. By considering the economic consequences, social impact, regional disparities, and potential avenues for compromise, policymakers can make informed decisions that promote both fair wages and sustainable economic growth. As discussions continue, finding common ground will be essential to ensure a more equitable and prosperous society for all.
